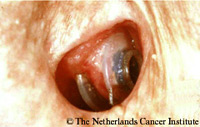
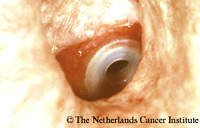
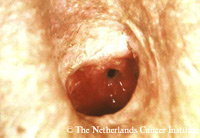
Prosthesis extruding from the fisula tractProblem: the prosthesis is extruding from the fistula tract.
Protrusion of the prosthesis and subsequent spontaneous extrusion is sometimes observed during an infection of the TE-fistula. This phenomenon has been also observed sometimes after (too) rapid downsizing of the prosthesis. Removal of the prosthesis is mandatory to avoid dislodgment into the trachea. Often the fistula tract is still patent and it is possible to ‘salvage’ the fistula and thus the voice by inserting a proper length device, either anterograde or retrograde. The figures show such a situation, in which the TEP could be salvaged: Figure 1. spontaneous extrusion; Figure 2. fistula tract after removal of prosthesis; Figure 3. insertion of a longer device; Figure 4. the well-healed fistula after 10 months, when the patient came for his next replacement for leakage through the device. If this is not possible, the fistula tract may close spontaneously secondary to the removal of the prosthesis and resolution of the infection, for which antibiotic treatment might be needed. Secondary re-puncturing is then necessary in order to re-establish the prosthetic voice. |